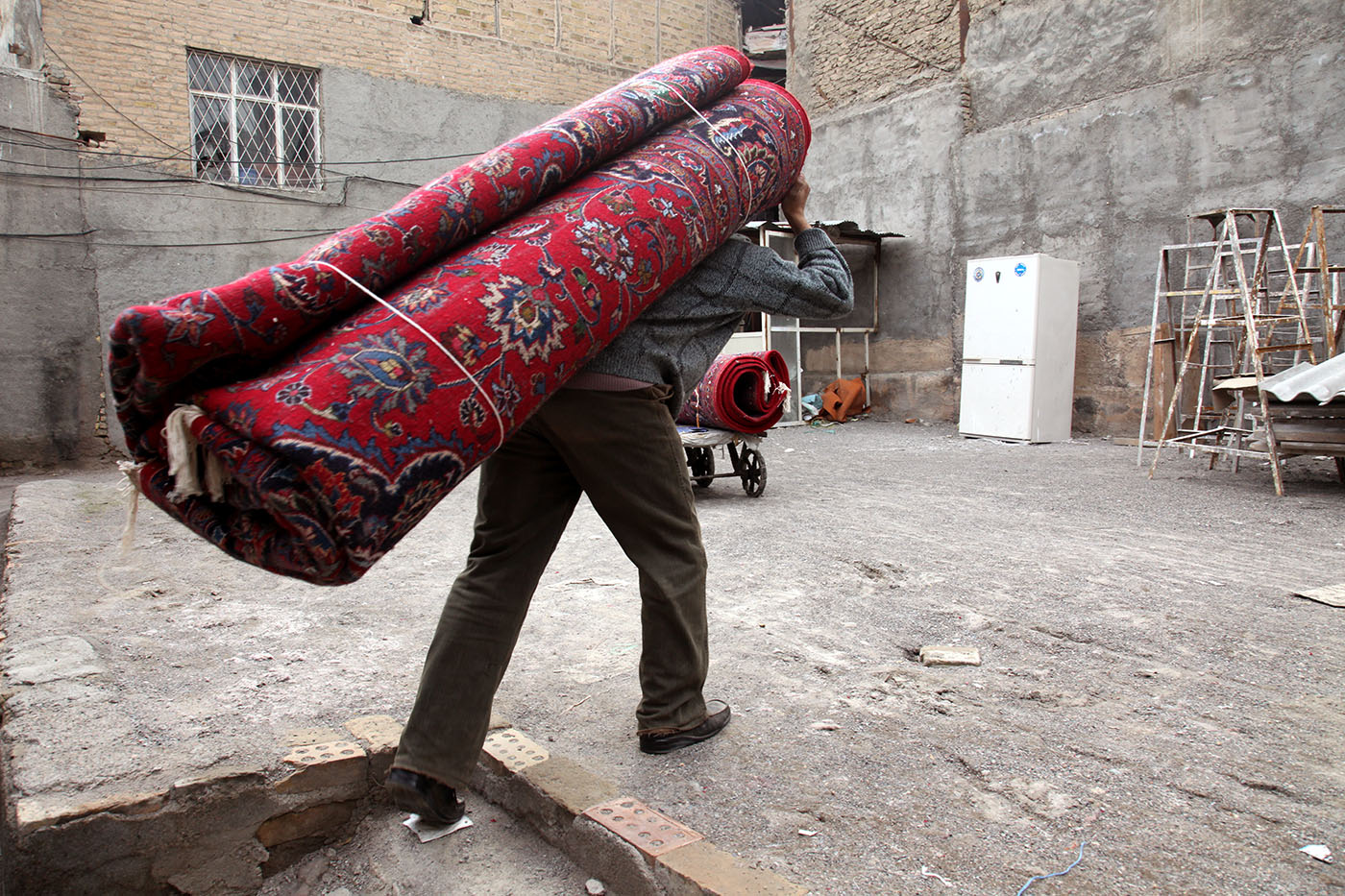
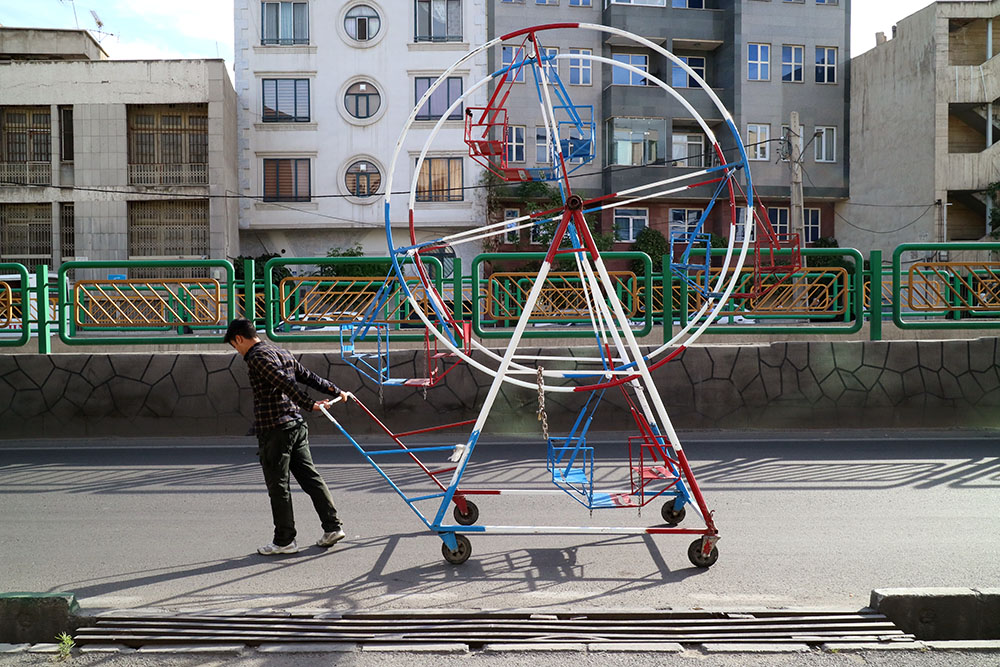
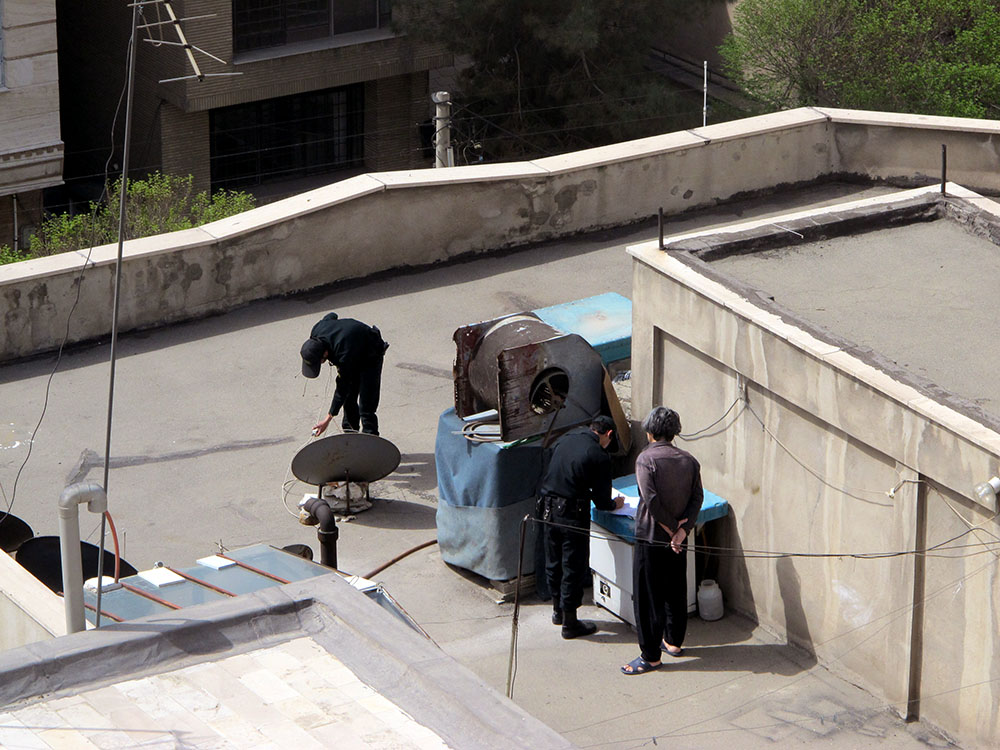
A man struggling under a giant carpet, a miniature mini-Ferris-wheel en transit, Iranian state agents removing an “illegal” satellite aerial — these are just a few of the images that illustrate the discussion of “Sanctions, Labor and Employment in Iran,” held by the Bourse & Bazaar Foundation. The online seminar also provided stark statistics about work in Iran in the time between the 2022 nationwide cost of living strikes and protests for Woman, Life, Freedom, which also began last year and continue until today. According to Pooya Alaedini, from the University of Tehran’s Faculty of Social Sciences, female unemployment rate in the first half of 2021–22 stood at 16.6 per cent, as opposed to 19.9 per cent in 2017–18. Unemployment rates also went down for men — 7.8 per cent in 2021–22 compared to 10.01 per cent in 2017–18. These falling rates, Alaedini maintained were not entirely good news; they had been influenced by Covid, which shrunk the overall numbers of people available to work, the result of the virus in other countries.
US sanctions against Iranian oil exports also significantly damaged jobs and living standards in the country. Government workers suffered under austerity measures the Islamic Republic imposed because of sanctions. Farmers and agricultural workers were the hardest hit, in part due to ongoing water shortages and drought.
During 2021–22, male participation in the labor force stood at 68.9 per cent. For women — despite high rates of university education — it was only 13.6 per cent.
For the young, between the ages of 18 and 35, unemployment figures were 16.6 per cent over the same period. While for women the same age, it was a whopping 28.3 per cent.
Importantly, participation for female college graduates in the labor force was 50.5 per cent against women’s overall labor force participation, at just 13.6 per cent. Even so, anecdotal evidence suggests that only low paying employment is available for highly educated women. So higher education, for women at least, was no guarantee of better paying jobs.
During the Bourse & Bazaar Foundation seminar, the political comparative historical sociologist Zep Kalb noted that the main participants in the cost of living and food protests were not Iran’s professional class, but farmers, contract workers (especially those in the oil and gas sector), teachers and pensioners. These 2021–22 figures were reported before the Woman Life Freedom protests rocked Iran, starting in the autumn of last year. In those nationwide demonstrations women were protesting against wearing the hijab as well as their lack of job and life opportunities.
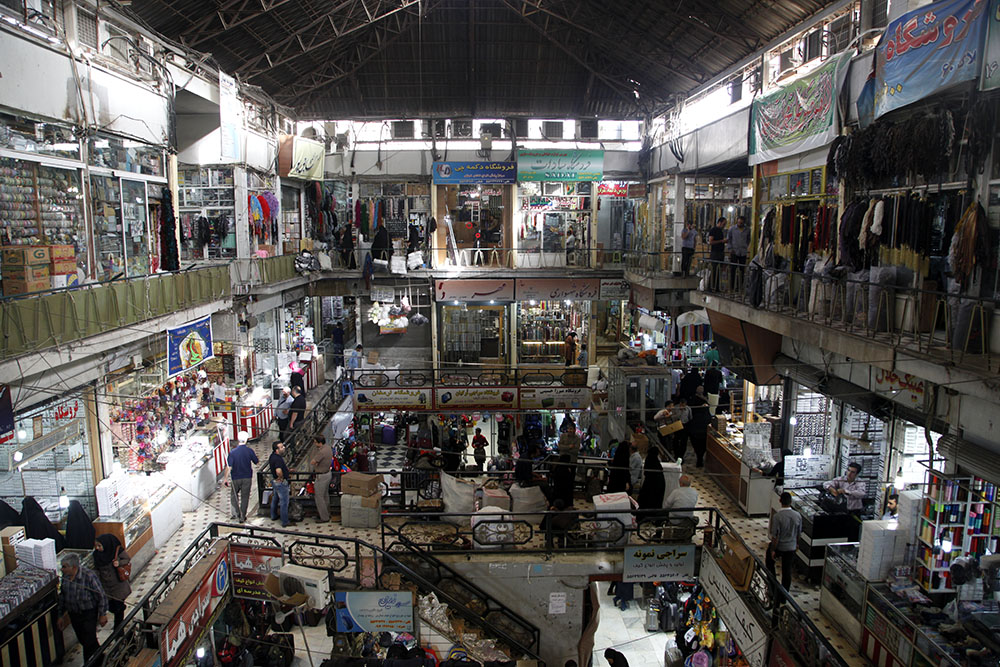
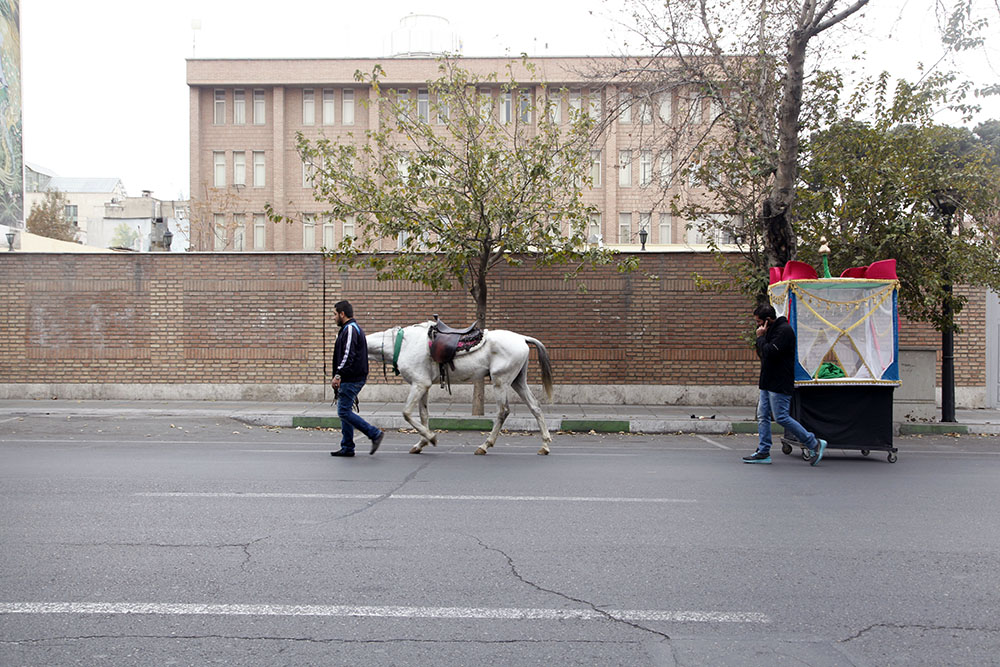
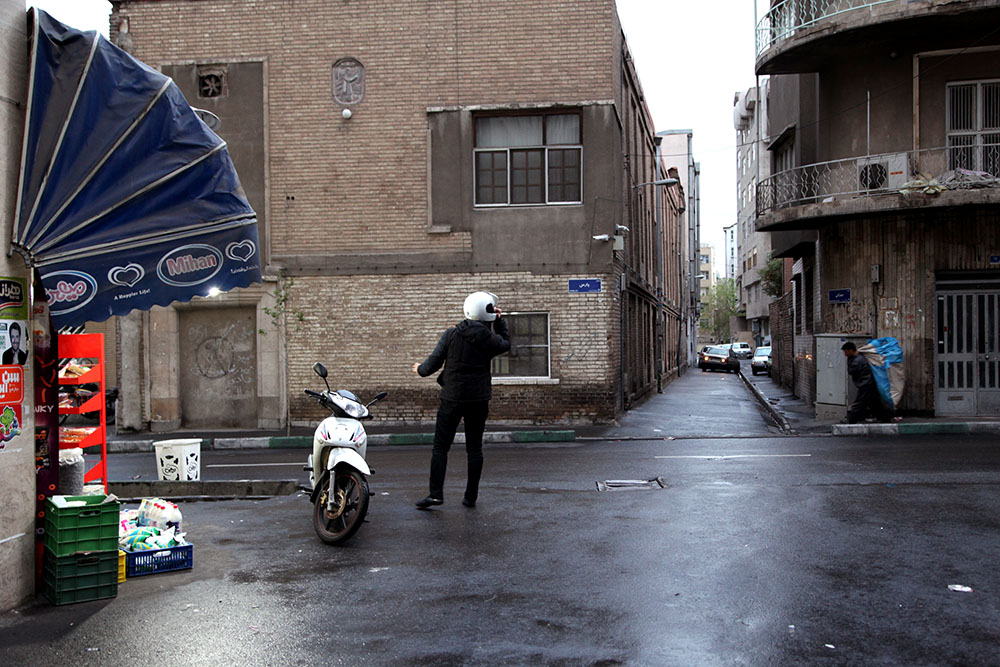
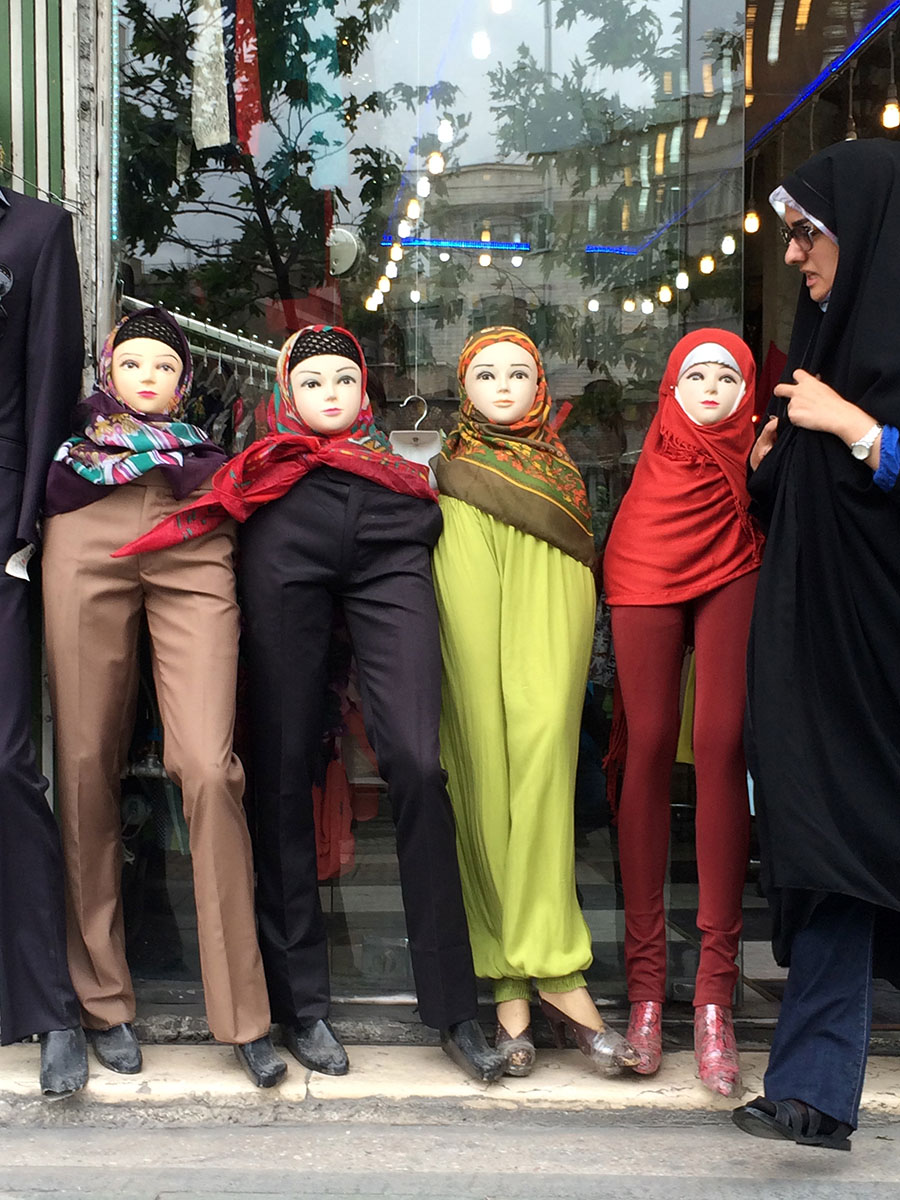
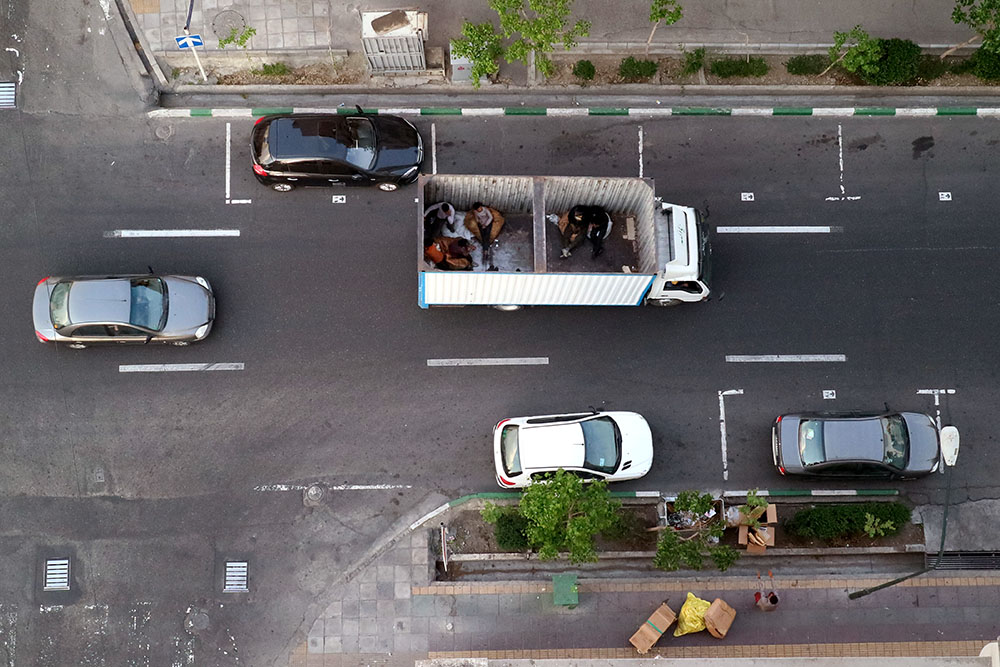
Peyman Hooshmandzadeh’s photographs of Iran at work do not show the professional classes at work in their private businesses, government offices or in health care. His view is rather from the street; ordinary people going about their daily lives and jobs, in the country’s capital, Tehran, and the tenth century religious city of Mashhad. Considering what the statistics reveal, it’s no wonder that women are seemingly absent.
—Malu Halasa











Captions for photographs translated from Persian by Salar Abdoh.
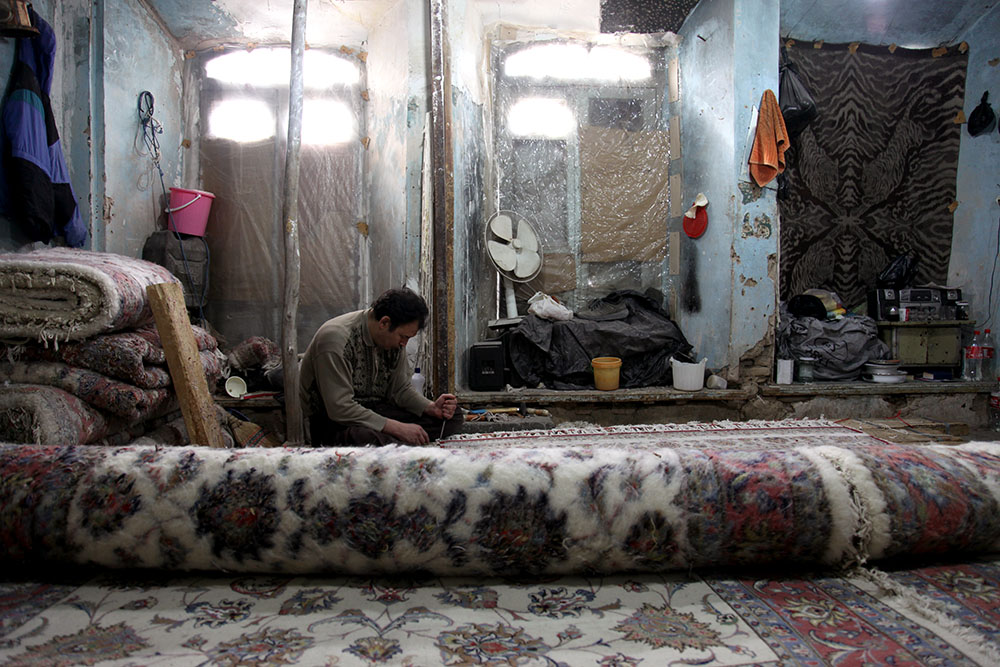
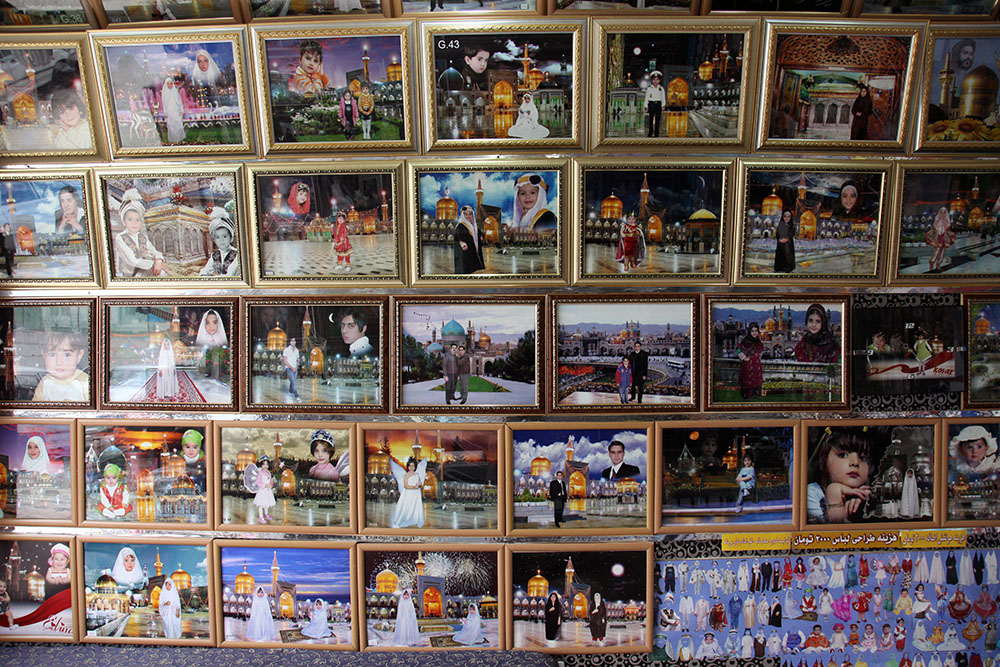
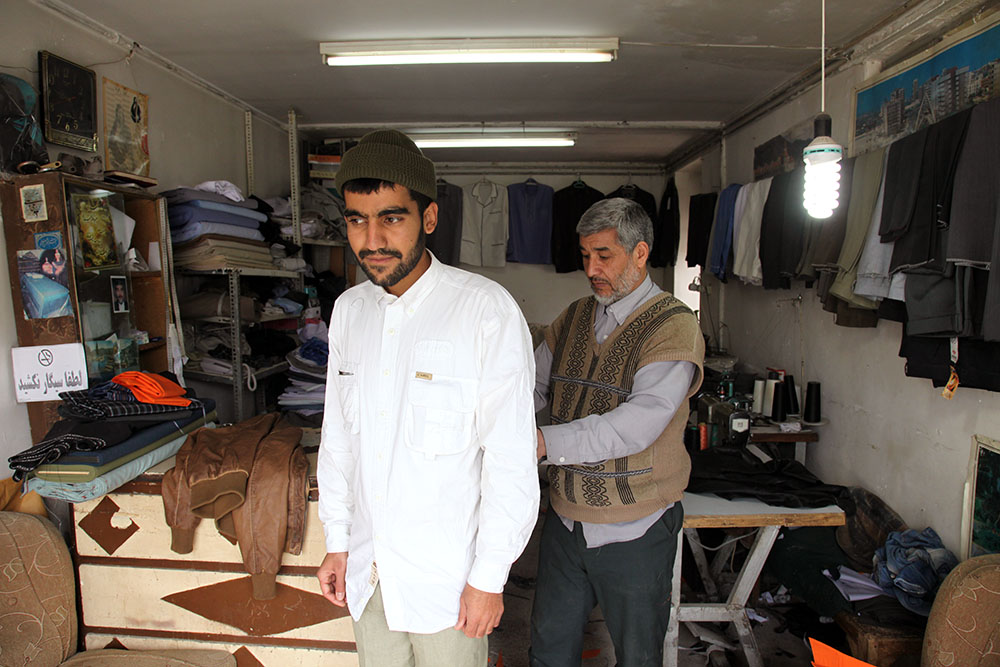
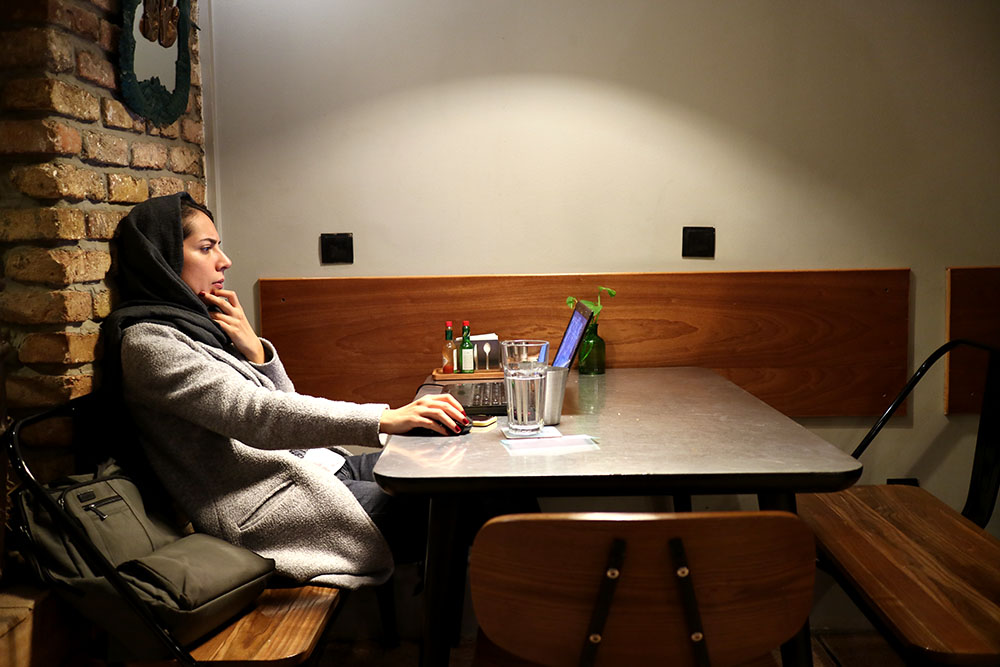















Love the compositions and colour palettes of these photos.